26 Aug 2021


A one-year-old female bearded dragon presented for a three-week history of inappetence, drinking less, lethargy, swelling and stiffness in the right hindleg.The veterinarian performed a fine needle aspirate of a lesion around the tibial tarsal joint on the same leg and submitted the slides to an external laboratory for cytological examination.
The aspirate from the joint lesion showed a pinkish (proteinaceous) background with small numbers of erythrocytes, some lysed cells, few large mononuclear cells with variably vacuolated cytoplasm (macrophages/synoviocytes) and rare heterophils.
Frequent light amber, needle-shaped structures, either individual or forming small aggregates (also called tophi), were noted and considered compatible with monosodium urate crystals. These were easier to appreciate by lowering the microscope condenser and increasing specimen contrast (Figure 1a – brown arrows) and even more when the slide was examined with a polarised light microscope (Figure 1b – crystals have a brilliant needle-shaped birefringent appearance).
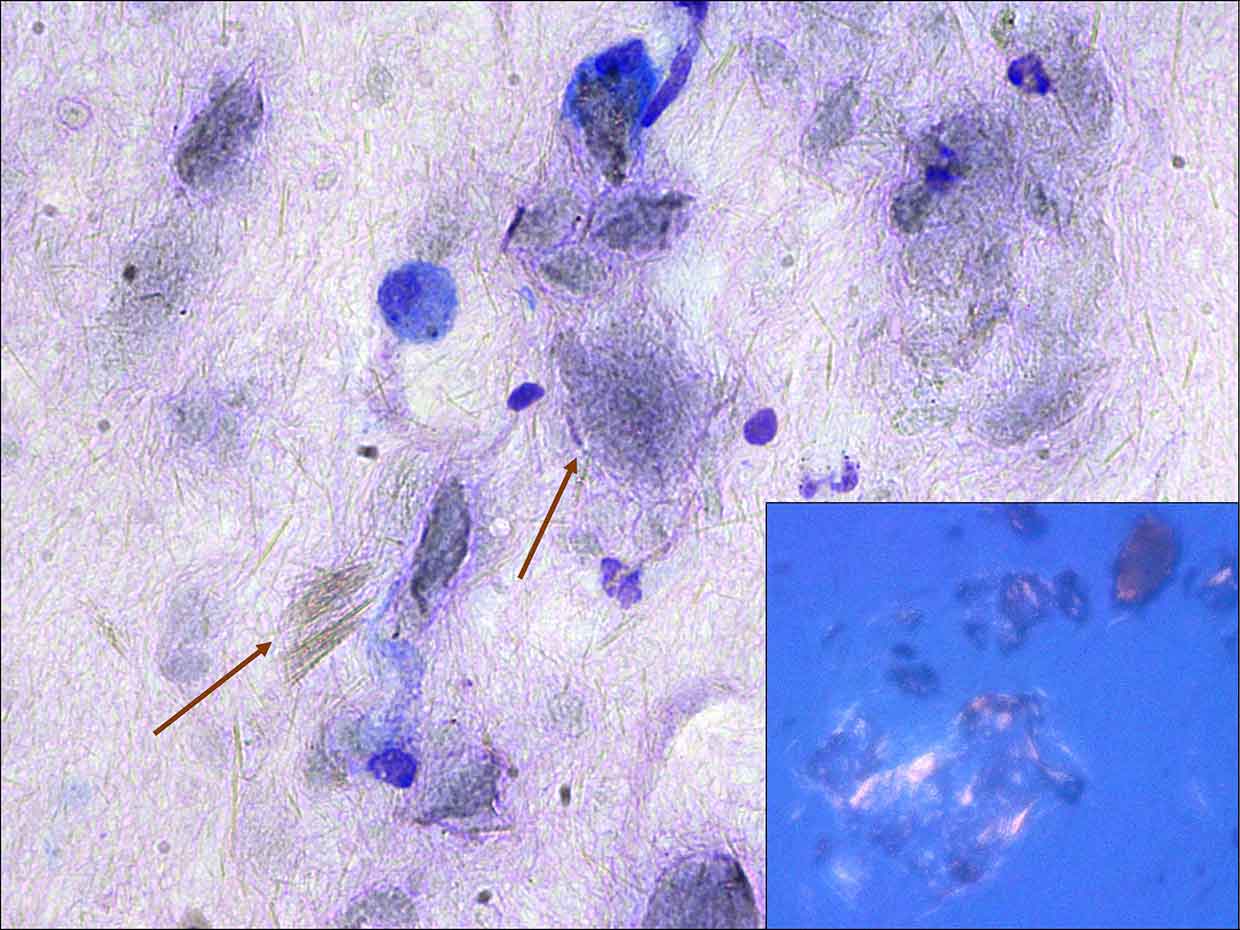
A diagnosis of articular gout was given.
After the diagnosis of gout was reached, a full haematology and biochemistry profile was performed. Uric acid was markedly increased (1,696µmol/L; reference range 95µmol/L to 678µmol/L) supporting renal disease, as the likely primary cause for gout.
The animal was treated with warm water soaks and allopurinol. Allopurinol inhibits the enzyme xanthine oxidase, decreasing degradation of xanthine to uric acid. Instead of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine are eliminated via the kidneys.
Warm water soaks are commonly performed to prevent dehydration, as more water is lost in the elimination of those substances in comparison to uric acid. Unfortunately, clinical signs significantly worsened in the following few weeks and the animal was euthanised.
No necropsy was performed; therefore, involvement of other visceral organs could not be assessed.
Gout is a disorder in which deposits of uric acid crystals accumulate in the body because of high blood levels (hyperuricaemia). Two main forms of gout have been reported:
The excess uric acid crystallises, forming an insoluble precipitate known as monosodium urate crystals at the level of joints (articular gout), SC tissues and often internal organs (visceral gout). The deposition of these crystals elicits an inflammatory response, and may affect organ function depending on anatomic location and extension. Over time, fibrosis and osteolysis may also occur.
Clinically, in articular gout, joints of the legs and feet may appear swollen, and/or nodules or masses may be seen on the toes or on the ribs. Articular gout is often looked at as a separate condition from visceral gout, but is likely to be an earlier presentation that precedes more widespread form.
Clinically, reptiles with visceral gout appear depressed, weak, thin, dehydrated, and often unwilling to move and eat. White to cream-coloured deposits (urate tophi) can sometimes be seen in the mouth.